Financial Decision-Making Frameworks
Financial decision-making frameworks take center stage, guiding individuals and organizations towards making informed choices that pave the way for success. Explore the world of financial decisions with confidence and clarity.
Discover how these frameworks empower decision-makers to navigate complexities and uncertainties, providing a solid foundation for robust financial strategies.
Overview of Financial Decision-Making Frameworks
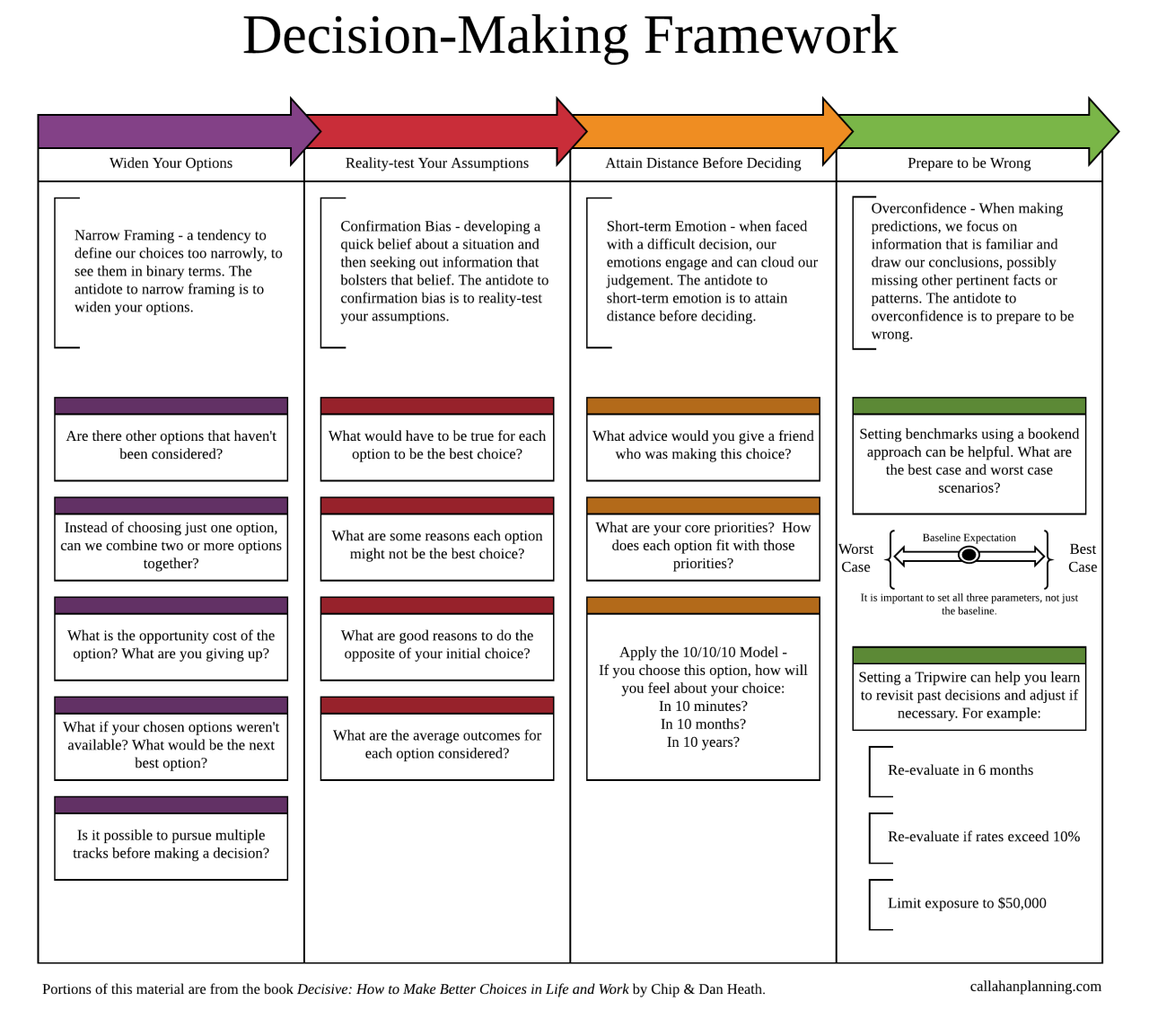
Financial decision-making frameworks are essential tools used by individuals and organizations to make informed choices about their finances. These frameworks provide a structured approach to analyzing financial options, weighing risks and benefits, and ultimately making decisions that align with specific goals and objectives. By utilizing these frameworks, decision-makers can minimize uncertainties and make sound financial choices that lead to long-term success.
Role of Financial Decision-Making Frameworks
- One commonly used financial decision-making framework is the Net Present Value (NPV) method, which helps in evaluating the profitability of an investment by comparing the present value of expected cash flows with the initial cost.
- Another popular framework is the Payback Period, which calculates the time it takes for an investment to recoup its initial cost through generated cash flows.
- The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a crucial framework that determines the rate of return at which the present value of cash inflows equals the present value of cash outflows.
Types of Financial Decision-Making Frameworks
Financial decision-making frameworks play a crucial role in helping organizations make informed choices about investments and projects. There are various types of frameworks used for this purpose, ranging from quantitative to qualitative approaches. Let’s explore some of the most common types of financial decision-making frameworks below.
Quantitative Frameworks
Quantitative frameworks involve the use of mathematical models and calculations to evaluate the financial viability of a project or investment. Two widely used quantitative frameworks are Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR).
- Net Present Value (NPV): NPV calculates the present value of cash inflows and outflows associated with a project to determine its profitability. A positive NPV indicates that the project is expected to generate value.
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR): IRR is the discount rate that makes the net present value of all cash flows from a particular project equal to zero. It helps in assessing the potential return of an investment.
Qualitative Frameworks
Qualitative frameworks focus on non-financial factors that can impact a decision. Some commonly used qualitative frameworks include SWOT analysis and Cost-Benefit Analysis.
- SWOT Analysis: SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This framework helps in identifying internal and external factors that can influence the success of a project or investment.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Cost-Benefit Analysis compares the costs and benefits of a decision or project, taking into account both monetary and non-monetary factors. It helps in evaluating whether the benefits outweigh the costs.
Comparison of Different Types of Frameworks
When comparing quantitative and qualitative financial decision-making frameworks, it’s essential to consider the strengths and limitations of each approach. While quantitative frameworks provide a clear numerical analysis of financial aspects, qualitative frameworks offer a more holistic view by considering non-financial factors. The combination of both quantitative and qualitative frameworks can provide a comprehensive evaluation of a decision, taking into account both financial and non-financial considerations.
Factors Influencing Financial Decision-Making
Financial decision-making is influenced by a variety of factors that play a crucial role in shaping the choices individuals and organizations make when it comes to managing their finances. Understanding these factors is essential for making informed and effective financial decisions.
One key factor that influences financial decision-making is risk tolerance. Risk tolerance refers to an individual’s or organization’s willingness to take on risk in pursuit of potential rewards. Those with a high risk tolerance may be more inclined to invest in higher-risk assets, while those with a low risk tolerance may prefer safer, more conservative investments.
Another important factor is financial goals. Financial goals provide a roadmap for decision-making by outlining what individuals or organizations hope to achieve with their finances. Whether it’s saving for retirement, purchasing a home, or starting a business, financial goals help guide decisions on saving, investing, and spending.
Additionally, the time horizon plays a significant role in financial decision-making. The time horizon refers to the length of time over which financial goals need to be achieved. Short-term goals may require different investment strategies than long-term goals, and the time horizon influences decisions on asset allocation and risk management.
External factors like economic conditions and regulations also impact financial decision-making. Economic conditions such as inflation, interest rates, and market volatility can affect investment returns and financial planning. Regulatory changes can impact tax strategies, investment options, and overall financial decision-making processes.
Behavioral biases also play a role in financial decision-making. These biases, such as loss aversion, overconfidence, and herd mentality, can lead to irrational decision-making and poor financial outcomes. Recognizing and mitigating these biases through education, awareness, and sound decision-making processes is essential for making informed financial choices.
Role of Behavioral Biases in Financial Decision-Making
Behavioral biases can significantly influence financial decision-making by leading individuals to make irrational choices based on emotions rather than logic. Understanding these biases and their impact is crucial for making informed decisions and achieving financial goals.
- Loss Aversion: This bias refers to the tendency for individuals to strongly prefer avoiding losses over acquiring gains of the same magnitude. This can lead to a reluctance to take necessary risks or make changes to investments, even when it may be beneficial in the long run.
- Overconfidence: Overconfidence bias occurs when individuals believe their abilities and knowledge are greater than they actually are. This can lead to excessive trading, poor investment choices, and a lack of diversification in portfolios.
- Herd Mentality: Herd mentality bias involves individuals following the actions of the majority without fully evaluating the situation. This can lead to buying high and selling low, as individuals may be swayed by the actions of others rather than conducting their own research.
By recognizing these behavioral biases and actively working to mitigate their influence, individuals and organizations can make more rational and informed financial decisions that align with their long-term goals and objectives.
Implementing Financial Decision-Making Frameworks
Implementing financial decision-making frameworks is a crucial step in ensuring that organizations make sound and strategic financial decisions. It involves a systematic approach that helps in analyzing, evaluating, and ultimately deciding on the best course of action. Below are the steps involved in applying a financial decision-making framework:
Step 1: Identify the Decision to Be Made, Financial decision-making frameworks
Before implementing a financial decision-making framework, it is essential to clearly identify the decision that needs to be made. This could range from investment decisions, budget allocation, risk management, or any other financial aspect that requires a strategic choice.
Step 2: Gather Relevant Data
Once the decision is identified, the next step is to gather all relevant data and information that will be crucial in the decision-making process. This data may include financial statements, market trends, economic indicators, and any other relevant information.
Step 3: Analyze the Data
After gathering the necessary data, it is important to analyze and evaluate the information to gain insights into the potential outcomes of each decision. This analysis will help in understanding the risks, benefits, and implications of each option.
Step 4: Develop Alternative Solutions
Based on the data analysis, it is crucial to develop alternative solutions or strategies that could address the financial decision at hand. These alternatives should be carefully evaluated based on their feasibility, risks, and alignment with organizational goals.
Step 5: Make the Decision
Once all alternatives have been evaluated, a decision must be made based on the analysis and insights gained from the process. The chosen option should align with the organization’s objectives and financial goals.
Real-World Examples
One successful implementation of a financial decision-making framework is the case of Apple Inc. The company’s strategic investment decisions, such as the introduction of new products or the acquisition of other companies, are based on a comprehensive financial analysis and evaluation process.
Challenges and Best Practices
Implementing financial decision-making frameworks can pose challenges such as data availability, complexity of analysis, and organizational resistance to change. To overcome these challenges, organizations should ensure clear communication, involve key stakeholders in the decision-making process, and continuously evaluate and refine the framework based on feedback and results.
FAQ Compilation
How do financial decision-making frameworks benefit individuals and organizations?
Financial decision-making frameworks provide a structured approach to making sound financial choices, leading to improved outcomes and long-term success.
What are some common examples of financial decision-making frameworks?
Examples include Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), SWOT analysis, and Cost-Benefit Analysis.
How can behavioral biases impact financial decision-making?
Behavioral biases can cloud judgment and lead to irrational decisions. Recognizing and mitigating these biases is crucial for effective decision-making.




