Financial Investment Portfolio Diversification Strategies
Financial investment portfolio diversification strategies are essential for maximizing your investment potential and minimizing risks. By exploring different asset classes and implementing effective diversification techniques, investors can secure a stable and profitable portfolio.
This comprehensive guide will delve into various strategies, types of investment instruments, and the importance of rebalancing and monitoring a diversified portfolio to help you make informed decisions and achieve long-term financial success.
Overview of Financial Investment Portfolio Diversification
Portfolio diversification is the practice of spreading investments across different assets to reduce risk and optimize returns. By diversifying a financial portfolio, investors can potentially minimize the impact of market fluctuations on their overall investment performance.
Benefits of Portfolio Diversification
- Diversification helps in reducing the overall risk of the portfolio by not putting all eggs in one basket. When one asset class underperforms, others may offset the losses.
- It can enhance the consistency of returns over time, as different asset classes have varying levels of sensitivity to market conditions.
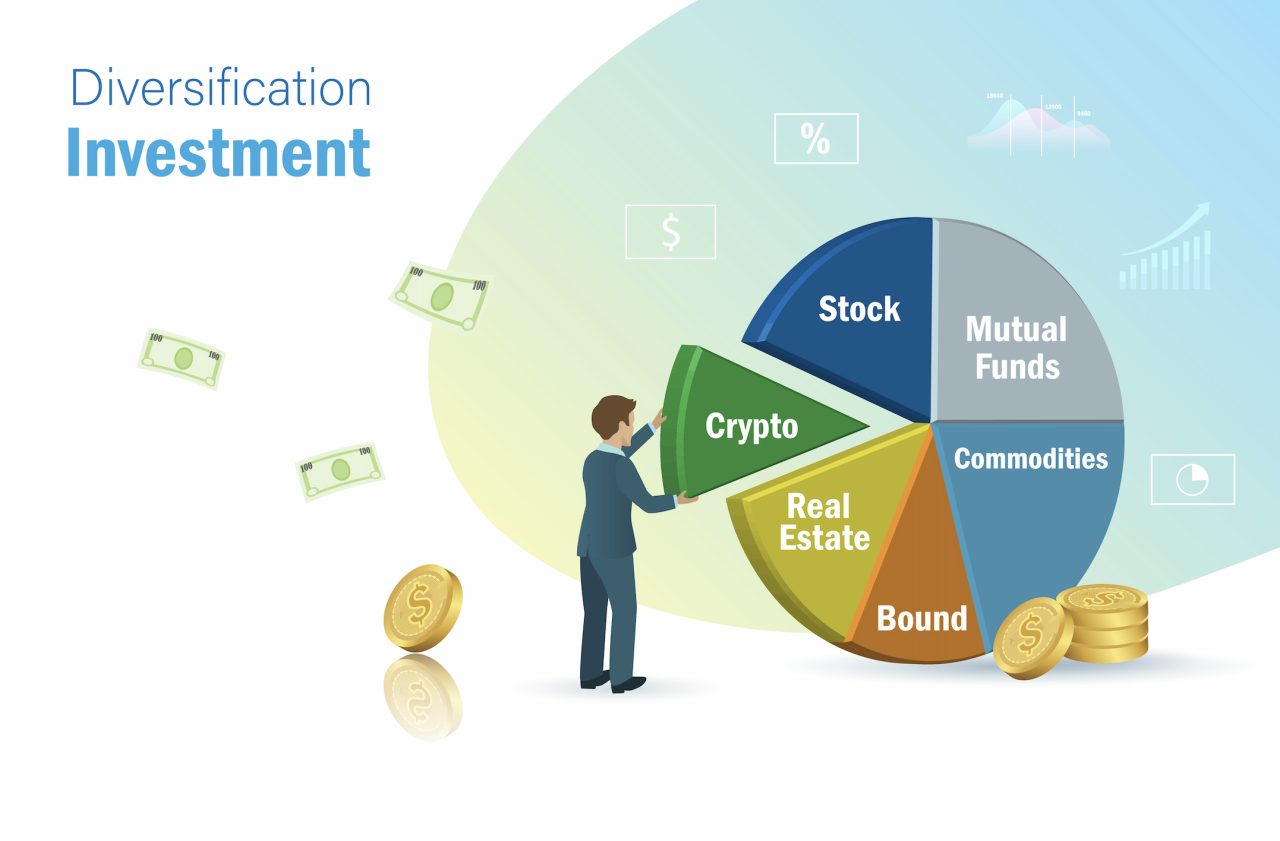
- Portfolio diversification can provide exposure to a wide range of investment opportunities, including stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and more.
Examples of Asset Classes for Diversification
- Stocks: Investing in a mix of large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks across different sectors.
- Bonds: Including government bonds, corporate bonds, and municipal bonds with varying maturities and credit ratings.
- Real Estate: Allocating funds to real estate investment trusts (REITs) or physical properties to diversify beyond traditional securities.
- Commodities: Adding exposure to commodities like gold, silver, oil, or agricultural products for inflation protection and portfolio diversification.
Strategies for Portfolio Diversification

When it comes to building a strong investment portfolio, diversification is key. By spreading your investments across different assets, you can reduce risk and potentially increase returns. Let’s explore some essential strategies for effective portfolio diversification.
Asset Allocation:
Asset allocation is the process of dividing your investments among different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities. The goal is to create a well-balanced portfolio that can weather market fluctuations. By spreading your investments across various asset classes, you can reduce the impact of volatility in any one sector.
Risk Management:
Risk management is crucial in diversification strategies. By carefully assessing and managing the risks associated with each investment, you can protect your portfolio from significant losses. Diversifying your investments can help mitigate risk by spreading it across different assets with varying levels of risk and return potential.
Geographical Diversification:
Geographical diversification involves investing in assets from different regions around the world. By spreading your investments across various countries and regions, you can reduce the impact of localized economic downturns or geopolitical events. This strategy can help protect your portfolio from the risks associated with a single country or region.
Impact of Geographical Diversification
Geographical diversification can provide several benefits to your investment portfolio:
- Reduced exposure to country-specific risks: By investing in assets from different countries, you can minimize the impact of economic or political events in any one region.
- Increased access to global opportunities: Diversifying geographically allows you to access a broader range of investment opportunities that may not be available in your home country.
- Enhanced risk-adjusted returns: By spreading your investments across different regions, you can potentially improve your portfolio’s risk-adjusted returns.
Types of Investment Instruments for Diversification
When it comes to diversifying your investment portfolio, there are various types of investment instruments to consider. Each type has its own unique characteristics and benefits, so it’s important to understand how they can help you achieve your diversification goals.
Stocks, Bonds, Mutual Funds, and ETFs
- Stocks: Stocks represent ownership in a company and can offer high returns but also come with high volatility. They are a common choice for investors looking for growth opportunities.
- Bonds: Bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations. They are considered safer than stocks and provide a steady income stream through regular interest payments.
- Mutual Funds: Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. They offer professional management and diversification benefits.
- ETFs: Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are similar to mutual funds but trade on stock exchanges like individual stocks. They offer diversification, low costs, and liquidity.
Alternative Investments, Financial investment portfolio diversification strategies
- Real Estate: Investing in real estate can provide diversification by adding a physical asset to your portfolio. Real estate investments can generate rental income and offer potential for appreciation.
- Commodities: Commodities such as gold, silver, oil, and agricultural products can act as a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainties. They can add diversification to a portfolio focused on traditional securities.
- Cryptocurrencies: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have gained popularity as alternative investments. They are highly volatile but can offer diversification benefits and potential for high returns.
It’s important to consider your risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon when choosing the right mix of investment instruments for diversification.
Rebalancing and Monitoring a Diversified Portfolio: Financial Investment Portfolio Diversification Strategies
When it comes to maintaining a diversified portfolio, one key aspect to consider is the process of rebalancing and monitoring. This involves periodically reviewing your investments and making adjustments to ensure they align with your desired asset allocation and risk tolerance.
Rebalancing Process
- Rebalancing involves selling overperforming assets and buying underperforming ones to bring your portfolio back to its original target allocation.
- It helps to control risk by preventing your portfolio from becoming too concentrated in a particular asset class.
- Regularly rebalancing ensures that your portfolio remains diversified and in line with your investment goals.
Frequency of Rebalancing
- Guidelines suggest rebalancing your portfolio at least once a year to maintain diversification.
- However, some investors prefer to rebalance more frequently, such as quarterly or semi-annually, especially during periods of market volatility.
- It is essential to assess your financial goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions when deciding how often to rebalance your portfolio.
Monitoring Portfolio Performance
- Monitoring the performance of different assets within your diversified portfolio is crucial to ensure they are meeting your expectations.
- Regularly reviewing your investments allows you to identify any underperforming assets that may require adjustments.
- By tracking the performance of your portfolio, you can make informed decisions on when to rebalance and reallocate your investments.
FAQ Resource
What is the significance of portfolio diversification?
Portfolio diversification helps spread risk across different asset classes, reducing the impact of market fluctuations on your investments.
How often should I rebalance my diversified portfolio?
It is recommended to rebalance your portfolio annually or whenever there are significant changes in the market or your financial goals.
Can alternative investments like cryptocurrencies be part of a diversified portfolio?
Yes, alternative investments like cryptocurrencies can add diversification benefits, but they also come with higher volatility and risk.