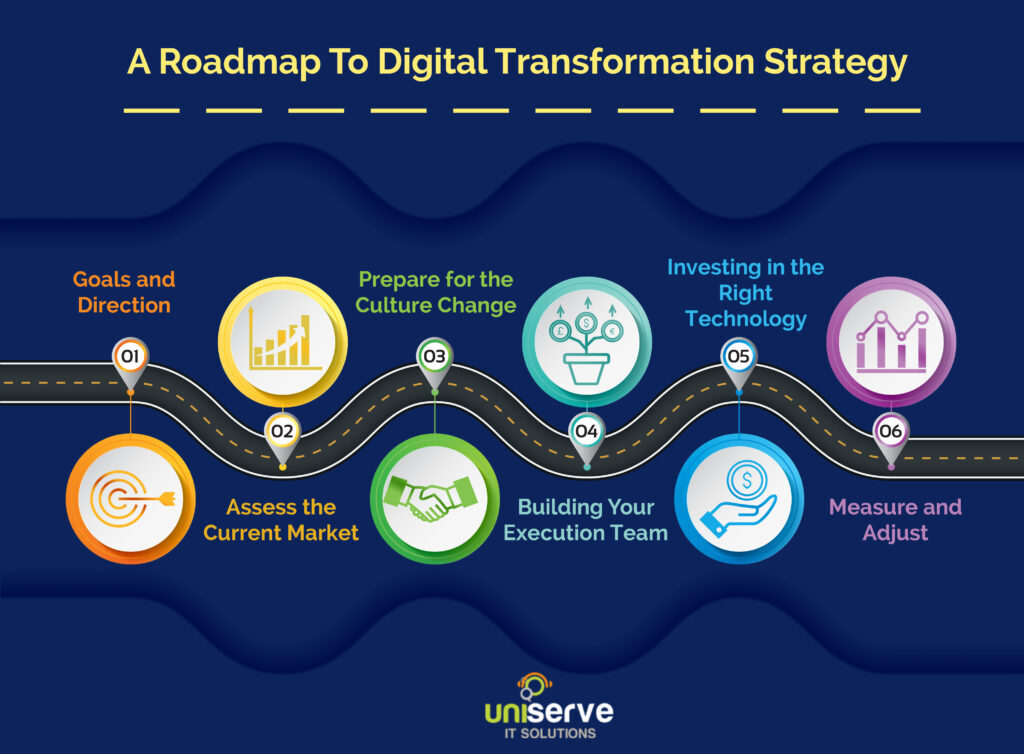
Financial Risk Mitigation Software Strategies
Financial risk mitigation software strategies set the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
As businesses navigate the complex landscape of financial risks, the implementation of robust software solutions becomes paramount to ensure resilience and success.
Overview of Financial Risk Mitigation Software: Financial Risk Mitigation Software Strategies
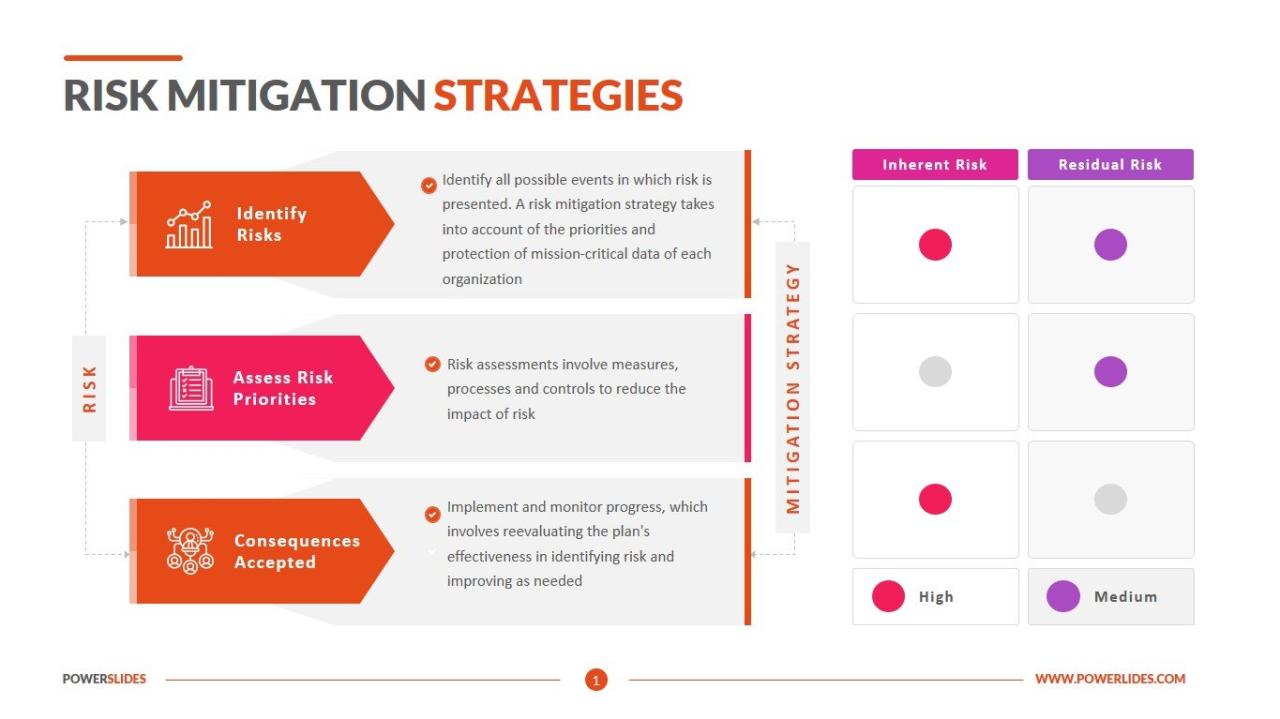
Financial risk mitigation software plays a crucial role in today’s business landscape by helping organizations identify, assess, and manage various types of risks that could potentially impact their financial stability. This software is designed to provide proactive measures to mitigate risks and protect the organization’s assets.
Popular Financial Risk Mitigation Software
- Oracle Financial Services
- SAS Risk Management
- IBM Algo Risk
- Quantifi
Key Features and Functionalities, Financial risk mitigation software strategies
- Real-time risk monitoring
- Scenario analysis and stress testing
- Compliance management
- Automated reporting
Benefits of Implementing Financial Risk Mitigation Software
- Enhanced risk visibility
- Improved decision-making processes
- Cost reduction through automated processes
- Regulatory compliance
Strategies for Implementing Financial Risk Mitigation Software

Implementing financial risk mitigation software is a crucial step for any company looking to protect its assets and minimize potential losses. Here are some strategies to consider:
Selection of the Right Financial Risk Mitigation Software
When selecting the right financial risk mitigation software for your company, it is essential to consider factors such as the specific needs of your organization, the features offered by the software, and the reputation of the vendor. Conduct thorough research, request demos, and involve key stakeholders in the decision-making process to ensure the software aligns with your risk management goals.
Integration into Existing Systems
Integrating financial risk mitigation software into existing systems can streamline processes and enhance efficiency. Best practices include conducting a thorough assessment of current systems, collaborating with IT experts to ensure compatibility, and providing adequate training to employees to facilitate a smooth transition.
Training Employees
Training employees to effectively use financial risk mitigation software is crucial for successful implementation. Develop comprehensive training programs that cover the features and functionalities of the software, provide hands-on practice sessions, and offer continuous support to address any challenges or questions that may arise.
Development of Customized Risk Mitigation Strategy
Utilizing financial risk mitigation software allows companies to develop customized risk mitigation strategies tailored to their specific needs. Leverage the data and analytics provided by the software to identify potential risks, assess their impact, and implement proactive measures to mitigate them effectively.
Risk Assessment and Monitoring with Financial Risk Mitigation Software
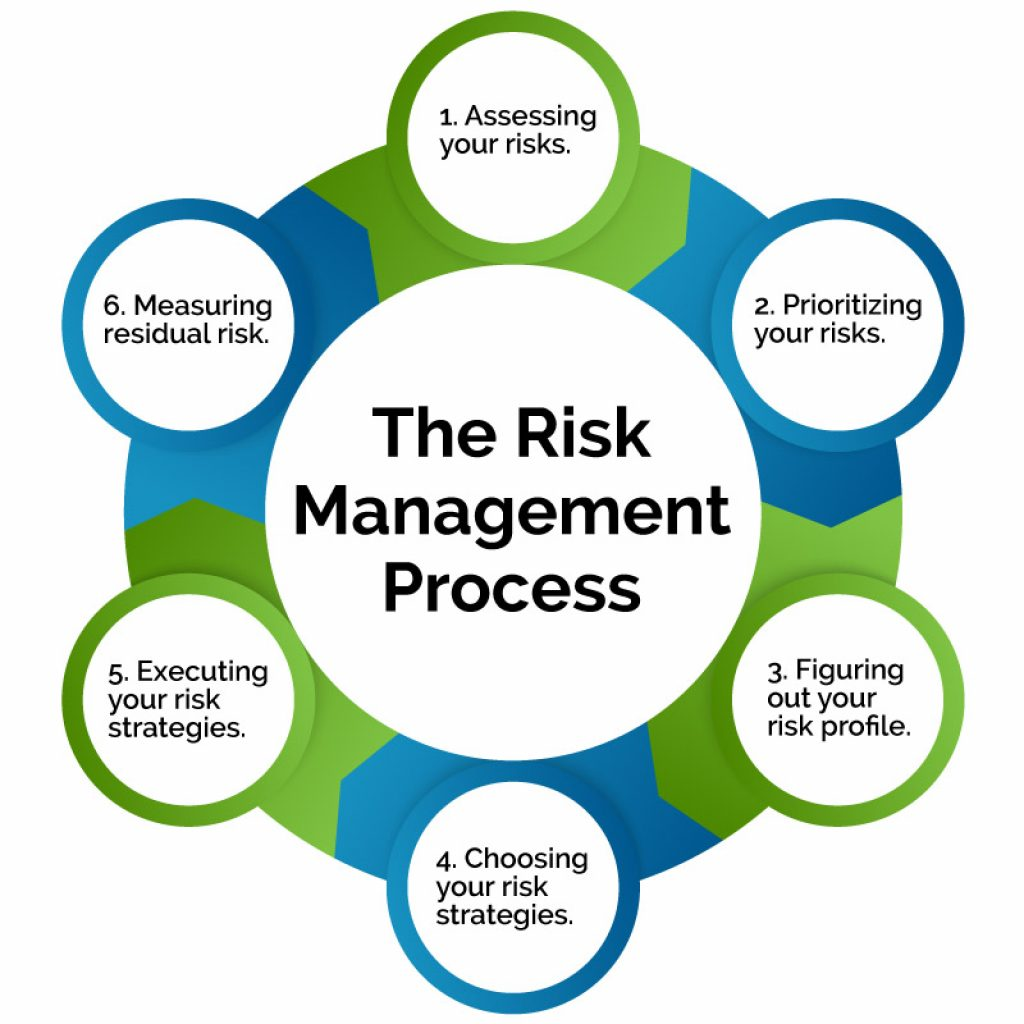
Risk assessment and monitoring are crucial aspects of managing financial risks effectively. Financial risk mitigation software plays a key role in helping organizations identify, prioritize, and monitor risks in real-time. By leveraging the capabilities of this software, businesses can proactively address potential threats and safeguard their financial health.
Conducting Risk Assessments
One of the primary functions of financial risk mitigation software is to conduct comprehensive risk assessments. This involves analyzing various factors such as market trends, economic indicators, regulatory changes, and internal processes to identify potential risks. The software uses advanced algorithms and data analytics to assess the likelihood and impact of these risks on the organization.
Identifying and Prioritizing Risks
Financial risk mitigation software helps in identifying and prioritizing risks by categorizing them based on their severity and potential impact on the business. By assigning risk scores and rankings, the software enables organizations to focus their resources on addressing high-priority risks first. This ensures that critical threats are mitigated effectively, reducing the overall risk exposure of the organization.
Real-time Monitoring of Risks
Real-time monitoring is essential for staying ahead of evolving risks and threats. Financial risk mitigation software continuously monitors key risk indicators and alerts users to any deviations from expected values. This proactive approach enables organizations to take immediate action to mitigate risks before they escalate into significant problems. Real-time monitoring also allows for timely decision-making and ensures that risk mitigation strategies are effective and efficient.
Utilizing Alerts and Notifications
Financial risk mitigation software utilizes alerts and notifications to keep stakeholders informed about potential risks and issues. These alerts can be customized based on predefined thresholds or triggers, ensuring that relevant parties are notified promptly when risks exceed acceptable levels. By leveraging alerts and notifications, organizations can take timely corrective actions and prevent potential losses or disruptions to their operations.
Compliance and Regulatory Aspects in Financial Risk Mitigation Software
In the realm of financial risk mitigation software, compliance and regulatory aspects play a crucial role in ensuring that organizations adhere to the necessary guidelines and standards set forth by governing bodies. Let’s delve into how financial risk mitigation software aids in managing regulatory requirements and maintaining compliance.
Role of Financial Risk Mitigation Software in Ensuring Compliance
Financial risk mitigation software serves as a valuable tool for organizations to ensure compliance with regulations by automating processes, tracking activities, and generating reports that demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements. By centralizing risk data and providing real-time updates, the software enables organizations to stay on top of changing regulations and implement necessary measures to remain compliant.
Examples of How Software Assists in Audit Trails and Reporting
– Financial risk mitigation software allows for the creation of detailed audit trails that document every action taken within the system, providing a comprehensive overview of risk management activities.
– The software generates customizable reports that highlight areas of non-compliance, flag potential risks, and showcase mitigation strategies implemented to address regulatory concerns.
– By facilitating easy access to historical data and real-time monitoring capabilities, the software streamlines the audit process and ensures that organizations can quickly respond to regulatory inquiries.
Significance of Data Security and Privacy Features
Data security and privacy features are paramount in compliance management, especially in the realm of financial risk mitigation software. These features ensure that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access, safeguarding against data breaches and maintaining confidentiality. By implementing robust security measures, organizations can instill trust in stakeholders and demonstrate their commitment to compliance with regulatory requirements.
Query Resolution
How can financial risk mitigation software benefit businesses?
Financial risk mitigation software can help businesses identify, assess, and manage potential risks effectively, leading to enhanced decision-making and overall operational efficiency.
What are the key features to look for in financial risk mitigation software?
Key features include risk assessment tools, real-time monitoring capabilities, compliance management modules, customizable risk mitigation strategies, and robust data security measures.
How can employees be trained to effectively use financial risk mitigation software?
Employee training programs should focus on familiarizing users with the software interface, conducting risk assessments, interpreting alerts and notifications, and implementing risk mitigation strategies.