Innovative Blockchain Technology Adoption Strategies
Innovative Blockchain Technology Adoption Strategies are transforming industries and empowering organizations to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, transparency, and security. This guide delves into the benefits, case studies, challenges, and best practices associated with adopting blockchain technology, providing a comprehensive roadmap for businesses looking to harness its transformative power.
As we explore the types of blockchain technology, its adoption framework, and key metrics for measuring success, you’ll gain invaluable insights into how to navigate the complexities of blockchain implementation. Embrace the future and unlock the potential of this groundbreaking technology with our expert guidance.
Innovative Blockchain Technology Adoption Strategies
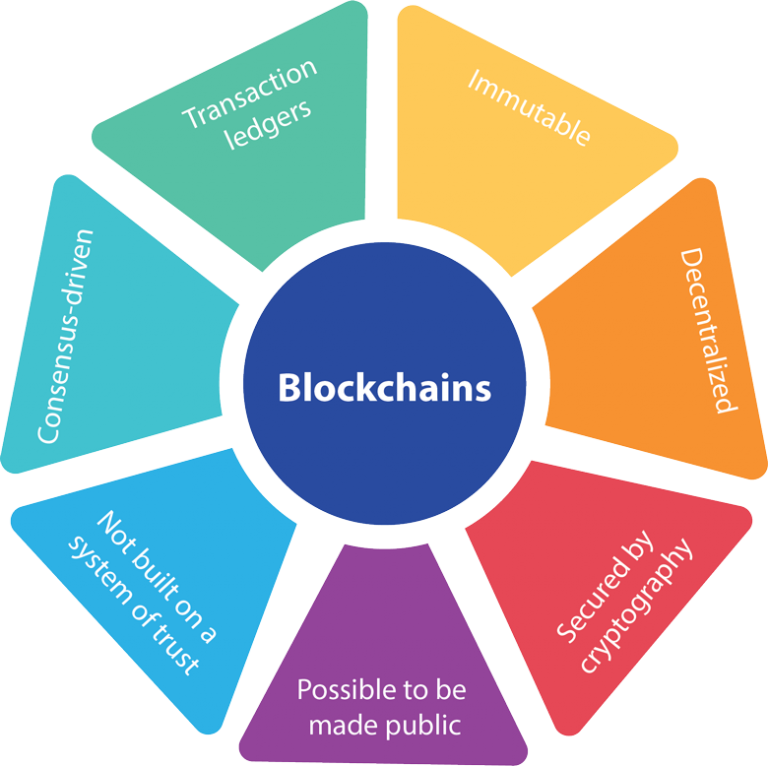
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, innovative blockchain technology adoption has emerged as a transformative force, revolutionizing industries and unlocking unprecedented opportunities. By leveraging the inherent benefits of blockchain, such as decentralization, transparency, and immutability, organizations can streamline processes, enhance security, and create new value streams.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology Adoption
- Decentralization: Eliminates intermediaries, empowering users with direct control over their data and transactions.
- Transparency: Provides a shared, immutable ledger that allows all participants to view and verify transactions.
- Immutability: Ensures that once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, safeguarding data integrity.
- Security: Employs advanced encryption and consensus mechanisms to protect data from unauthorized access and tampering.
- Efficiency: Automates processes, reduces paperwork, and streamlines operations, leading to significant cost savings.
Case Studies of Successful Blockchain Technology Adoption
- Supply Chain Management: Walmart uses blockchain to track food products from farm to store, ensuring transparency and traceability.
- Financial Services: Ripple’s blockchain solution enables fast and secure cross-border payments, reducing transaction costs and delays.
- Healthcare: VeChain provides a blockchain platform for healthcare data management, enhancing patient privacy and improving interoperability.
- Government: Estonia has implemented blockchain-based digital identity systems, simplifying citizen services and reducing bureaucracy.
- Entertainment: Dapper Labs’ Flow blockchain supports the popular NBA Top Shot platform, allowing fans to collect and trade digital collectibles.
Challenges of Adopting Blockchain Technology
- Scalability: Handling large volumes of transactions can be a challenge for some blockchain platforms.
- Interoperability: Ensuring seamless integration between different blockchain networks can be complex.
- Regulation: Evolving regulatory frameworks can create uncertainty for businesses exploring blockchain adoption.
- Technical Expertise: Implementing and managing blockchain solutions requires specialized technical knowledge.
- Cost: Developing and maintaining blockchain-based systems can be resource-intensive.
Types of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we store and manage data. There are different types of blockchain technology, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
The three main types of blockchain technology are public blockchains, private blockchains, and consortium blockchains.
Public Blockchains
Public blockchains are open and accessible to everyone. Anyone can join the network and participate in the validation and consensus process. Public blockchains are transparent and immutable, meaning that all transactions are recorded on the blockchain and cannot be altered or deleted.
Examples of public blockchains include Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin.
Advantages of public blockchains include:
- Transparency and immutability
- Decentralization
- Security
Disadvantages of public blockchains include:
- Scalability issues
- High transaction fees
- Slow transaction times
Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are permissioned blockchains that are controlled by a single organization or group of organizations. Only authorized participants can join the network and participate in the validation and consensus process.
Examples of private blockchains include Hyperledger Fabric and R3 Corda.
Advantages of private blockchains include:
- Scalability
- Lower transaction fees
- Faster transaction times
Disadvantages of private blockchains include:
- Less transparency and immutability
- Centralization
- Security risks
Consortium Blockchains, Innovative blockchain technology adoption strategies
Consortium blockchains are semi-permissioned blockchains that are controlled by a group of organizations. Only authorized participants can join the network and participate in the validation and consensus process.
Examples of consortium blockchains include the Ethereum Enterprise Alliance and the Hyperledger Consortium.
Advantages of consortium blockchains include:
- Scalability
- Lower transaction fees
- Faster transaction times
- Increased transparency and immutability
Disadvantages of consortium blockchains include:
- Less decentralization
- Security risks
Blockchain Technology Adoption Framework
To successfully adopt blockchain technology, it’s essential to have a structured framework in place. This framework should Artikel the key phases involved in the adoption process and provide a timeline for each phase.
Phases of Blockchain Adoption Framework
- Assessment and Planning: Define the business goals, conduct a technology assessment, and develop a roadmap for adoption.
- Proof of Concept (PoC): Implement a small-scale project to demonstrate the feasibility and benefits of blockchain.
- Pilot Deployment: Expand the PoC to a larger scale to gather real-world data and refine the solution.
- Full-Scale Implementation: Deploy the blockchain solution across the organization and integrate it with existing systems.
- Continuous Improvement: Monitor the performance of the blockchain solution, make necessary adjustments, and explore new use cases.
The timeline for each phase will vary depending on the size and complexity of the organization and the specific blockchain solution being adopted. However, it’s important to establish a realistic timeline to ensure that the adoption process is completed efficiently and effectively.
Blockchain Technology Adoption Metrics
Measuring the success of blockchain technology adoption requires tracking key metrics. These metrics provide insights into adoption progress, impact, and areas for improvement.
Data Collection and Analysis
Data collection methods include surveys, interviews, transaction monitoring, and analytics tools. Collected data should be analyzed using statistical techniques to identify trends, patterns, and correlations.
Blockchain Technology Adoption Best Practices: Innovative Blockchain Technology Adoption Strategies
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize a wide range of industries, from finance to healthcare to supply chain management. However, adopting blockchain technology can be a complex and challenging process. By following best practices, organizations can increase their chances of success.
One of the most important best practices is to start with a clear understanding of the business problem that you are trying to solve with blockchain. This will help you to identify the right blockchain platform and to develop a successful implementation strategy.
It is also important to build a strong team of experts who have experience with blockchain technology. This team will be responsible for developing and implementing your blockchain solution.
Finally, it is important to be patient and persistent. Blockchain technology is still a relatively new technology, and there will be challenges along the way. However, by following best practices, you can increase your chances of success.
Examples of Successful Blockchain Adoptions
There are a number of organizations that have successfully adopted blockchain technology. Some of these organizations include:
* Walmart: Walmart has used blockchain technology to improve the efficiency of its supply chain. The company has implemented a blockchain-based system that tracks the movement of goods from suppliers to stores. This system has helped Walmart to reduce costs and improve product quality.
* Maersk: Maersk is a global shipping company that has used blockchain technology to improve the efficiency of its shipping operations. The company has implemented a blockchain-based system that tracks the movement of goods from origin to destination. This system has helped Maersk to reduce costs and improve customer service.
* IBM: IBM is a global technology company that has used blockchain technology to develop a number of innovative solutions. These solutions include a blockchain-based system for managing digital identities and a blockchain-based system for tracking the provenance of goods.
Lessons Learned from Successful Blockchain Adoptions
There are a number of lessons that can be learned from the successful adoption of blockchain technology by these organizations. Some of these lessons include:
* Start with a clear understanding of the business problem that you are trying to solve with blockchain.
* Build a strong team of experts who have experience with blockchain technology.
* Be patient and persistent.
* Be willing to experiment.
* Be open to change.
By following these best practices, organizations can increase their chances of success when adopting blockchain technology.
FAQs
What are the key benefits of adopting blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology offers numerous benefits, including enhanced security, transparency, efficiency, cost reduction, and the ability to automate processes.
How can I measure the success of my blockchain adoption strategy?
Key metrics for measuring success include transaction volume, transaction speed, cost savings, and user adoption rates.
What are the challenges associated with adopting blockchain technology?
Challenges include scalability, interoperability, regulatory uncertainty, and the need for skilled professionals.