Risk Management Strategies
With Risk management strategies at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling journey filled with unexpected twists and insights. Risk management strategies are the cornerstone of business resilience and growth, ensuring that organizations navigate challenges effectively. From identifying potential risks to implementing proactive measures, this guide will explore the essential strategies that businesses need to thrive in today’s dynamic landscape.
Importance of Risk Management Strategies
Risk management strategies play a crucial role in the smooth operation of businesses. By identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks, companies can protect their assets, reputation, and financial stability.
Examples of Potential Risks
- Financial risks such as market fluctuations, credit risks, and liquidity issues
- Operational risks like supply chain disruptions, technology failures, and regulatory compliance issues
- Reputational risks from negative publicity, customer dissatisfaction, or unethical behavior
- Strategic risks such as competition, changing market trends, and mergers/acquisitions
Impact of Ineffective Risk Management
Effective risk management strategies are essential because the consequences of not having them in place can be severe. Businesses that fail to address risks may face financial losses, legal liabilities, damaged reputation, and even closure. By proactively managing risks, companies can improve decision-making, enhance resilience, and ensure long-term success.
Types of Risk Management Strategies
Risk management strategies play a crucial role in helping organizations navigate uncertainties and potential threats. There are various types of risk management strategies that organizations can implement to mitigate risks and protect their operations.
Risk Avoidance
Risk avoidance is a strategy where organizations choose to completely steer clear of activities or situations that could potentially lead to risks. By avoiding certain risks altogether, organizations aim to eliminate the possibility of negative outcomes. This strategy is often employed when the potential risks outweigh the benefits of pursuing a particular course of action.
Risk Reduction
Risk reduction involves taking proactive measures to minimize the impact or likelihood of risks occurring. This can include implementing safety protocols, conducting regular maintenance checks, or investing in technology to enhance security measures. By reducing risks, organizations can better protect themselves against potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Risk Sharing
Risk sharing is a strategy where organizations transfer a portion of the risk to another party. This can be done through insurance policies, contracts, or partnerships where the risk is distributed among multiple stakeholders. By sharing risks, organizations can mitigate the financial burden of potential losses and better manage uncertainties.
Risk Retention
Risk retention is a strategy where organizations accept and absorb the risks without transferring them to external parties. This can be a conscious decision made based on the organization’s risk tolerance and financial capabilities. By retaining risks, organizations take direct responsibility for managing and responding to potential threats.
Proactive vs. Reactive Risk Management Strategies
Proactive risk management strategies involve identifying and addressing risks before they occur, while reactive strategies focus on responding to risks after they have manifested. Proactive approaches allow organizations to anticipate and prepare for potential threats, reducing the likelihood of negative impacts. On the other hand, reactive strategies involve managing risks as they arise, often resulting in higher costs and damages.
Significance of Diversification, Risk management strategies
Diversification is a key risk management strategy that involves spreading investments, resources, or operations across a variety of assets or activities. By diversifying, organizations can reduce their exposure to any single risk and minimize the impact of potential losses. Diversification helps organizations maintain stability and resilience in the face of uncertainties and fluctuations in the market.
Implementing Risk Management Strategies
Implementing risk management strategies within an organization is crucial for ensuring the sustainability and success of the business. It involves a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks to develop effective mitigation plans.
Assessing and Prioritizing Risks
Before implementing risk management strategies, it is essential to assess and prioritize risks based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. This process helps in focusing on high-priority risks that could significantly impact the organization.
- Identify all potential risks relevant to the organization.
- Assess the impact of each risk on the business objectives and operations.
- Evaluate the likelihood of each risk occurring.
- Prioritize risks based on their severity and the organization’s risk tolerance.
Tools and Software for Risk Management
There are various tools and software available to assist organizations in implementing risk management strategies effectively. These tools provide functionalities for risk assessment, monitoring, and reporting, making the process more efficient and organized.
- Risk Management Software: Platforms like Risk Cloud, LogicManager, or Resolver offer comprehensive solutions for managing risks in real-time.
- Risk Assessment Tools: Tools like Riskalyze or RiskWatch help in evaluating risks and creating risk profiles for the organization.
- Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Systems: ERM systems like SAP GRC or Oracle Risk Management enable organizations to integrate risk management into their overall business processes.
Monitoring and Evaluating Risk Management Strategies
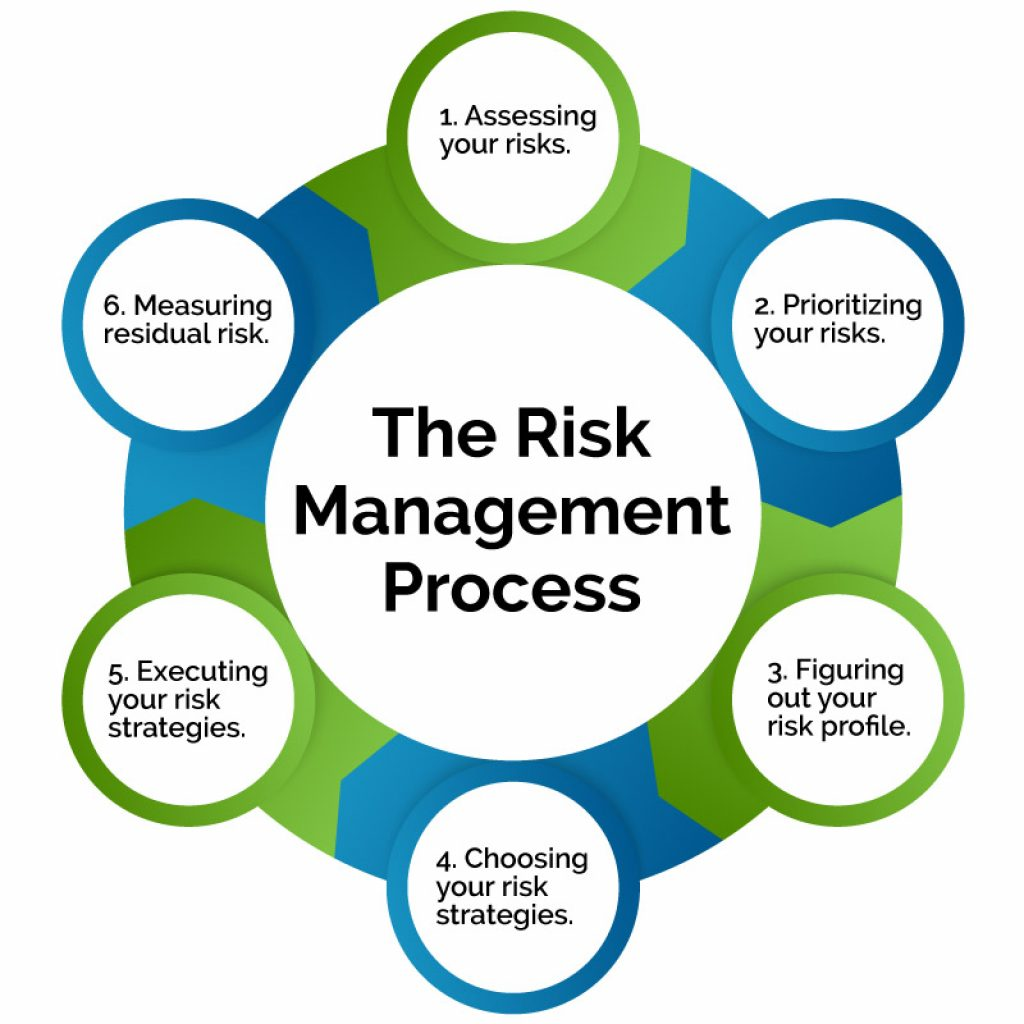
Regular monitoring and evaluation of risk management strategies are crucial for ensuring the effectiveness and relevance of the measures put in place. By continuously assessing and analyzing the strategies, organizations can identify potential gaps, weaknesses, or areas for improvement, ultimately enhancing their ability to mitigate risks.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Measuring Effectiveness
Key performance indicators (KPIs) serve as valuable metrics for measuring the success and impact of risk management strategies. Some common KPIs that can be used include:
- Frequency and severity of risks identified and addressed
- Reduction in financial losses due to risk incidents
- Compliance with regulatory standards and requirements
- Effectiveness of communication and training on risk management
- Response time to risk incidents and resolution
Adjusting Risk Management Strategies based on Evaluation Results
Upon evaluating the performance of risk management strategies, organizations should be prepared to adjust and refine their approaches to better address emerging risks and changing circumstances. Some best practices for adjusting risk management strategies include:
- Conducting regular reviews and assessments of risk management processes
- Engaging stakeholders and key personnel in the evaluation process
- Implementing feedback mechanisms to gather insights and suggestions for improvement
- Being proactive in anticipating and adapting to new risks and challenges
- Continuously updating risk management policies and procedures based on evaluation findings
Quick FAQs
Why are risk management strategies crucial for businesses?
Risk management strategies are crucial as they help businesses identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks, ensuring continuity and resilience.
What types of risk management strategies can businesses employ?
Businesses can employ strategies like risk avoidance, risk reduction, risk sharing, and risk retention to manage different types of risks effectively.
How can organizations prioritize risks for effective risk management?
Organizations can prioritize risks by assessing their impact and likelihood, focusing on addressing high-impact risks first.